Marvin "Popcorn" Sutton
Expert
- Joined
- Jul 25, 2021
- Messages
- 204
- Reaction score
- 308
- Points
- 63
It is always necessary to choose the house for the laboratory with special care, it is necessary to understand that the success of the entire enterprise depends on the place. Therefore, in this article, we will discuss some nuances that will help you in setting up a reliable laboratory.
When selectinging a laboratory space, consider the surrounding area. In the production process, it is possible to emit gases into the atmosphere, so it is necessary to consider that there will be various chemical odors near the house. Of course, we will try to avoid this, but it must be taken into account.
The road to the house should be well visible. Find an opportunity to install video cameras on the road towards the house, and that it does not make the neighbors suspicious. It is desirable to have a large area of the property where the lab is located so that outsiders can't drive by. Otherwise, you will have to get a high fence against prying eyes. In this case, it is a good option to arrange a laboratory on the farm. But in each case, the choice of space is an individual decision, depending on the combination of factors and capabilities of the organizer.
In order for the laboratory to function well, it must receive uninterrupted power and water supply. Therefore, include a backup supply of these two resources on your list in advance. It is a good idea to have several electric generators, with a fuel supply for them. Have a water station for water extraction, a filter system, and a tank to store some cubes of water.
Another important thing is to have a sewage system, preferably with a cleaning system. If your house has no sewage system, the waste will have to be removed, I recommend that you consider this issue as one of the mains, the accumulation of waste will create unnecessary danger to the entire enterprise. We will touch on this topic separately.
Let's move on to the room itself, or rather, it is desirable that there were several of them:
1) Laboratory. The main room, where one or more reactors and all the infrastructure for syntheses are located.
2) A room for drying, bottling and freezing of the final product.
3) Warehouse for storage of precursors and other chemicals.
Each room should be kept at a temperature of about 20 ºC, and air conditioners or heating boilers should be installed to maintain this temperature, depending on your region.
When selectinging a laboratory space, consider the surrounding area. In the production process, it is possible to emit gases into the atmosphere, so it is necessary to consider that there will be various chemical odors near the house. Of course, we will try to avoid this, but it must be taken into account.
The road to the house should be well visible. Find an opportunity to install video cameras on the road towards the house, and that it does not make the neighbors suspicious. It is desirable to have a large area of the property where the lab is located so that outsiders can't drive by. Otherwise, you will have to get a high fence against prying eyes. In this case, it is a good option to arrange a laboratory on the farm. But in each case, the choice of space is an individual decision, depending on the combination of factors and capabilities of the organizer.
In order for the laboratory to function well, it must receive uninterrupted power and water supply. Therefore, include a backup supply of these two resources on your list in advance. It is a good idea to have several electric generators, with a fuel supply for them. Have a water station for water extraction, a filter system, and a tank to store some cubes of water.
Another important thing is to have a sewage system, preferably with a cleaning system. If your house has no sewage system, the waste will have to be removed, I recommend that you consider this issue as one of the mains, the accumulation of waste will create unnecessary danger to the entire enterprise. We will touch on this topic separately.
Let's move on to the room itself, or rather, it is desirable that there were several of them:
1) Laboratory. The main room, where one or more reactors and all the infrastructure for syntheses are located.
2) A room for drying, bottling and freezing of the final product.
3) Warehouse for storage of precursors and other chemicals.
Each room should be kept at a temperature of about 20 ºC, and air conditioners or heating boilers should be installed to maintain this temperature, depending on your region.
A laboratory is a large room, about 20 square meters of space are suitable for a laboratory with a reactor. The ceiling height should be about 2.5 meters or higher to accommodate the reactor and attachments. The walls, floor and ceiling are best finished with large-format glazed tiles for easy cleaning. As a last resort, let it be plastic panels or thick plastic sheeting.
The laboratory must be as equipped as possible: hot and cold running water, sewerage, heating/air conditioning, good electrical power (calculated total capacity of all devices with reserve). A backup generator, preferably with autostart in case of mains voltage drop, or an uninterruptible power supply inverter (preferably both devices) should ensure uninterrupted power supply to the laboratory. In some phases of synthesis, a short power outage can mean loss of productivity and create an explosion or fire hazard situation.
In the laboratory you need to put a good system of supply and exhaust ventilation, and I recommend putting a motor for exhaust ventilation twice as powerful as it is necessary for your room.
Draw in advance a diagram of the arrangement of devices in your laboratory to conduct power, water and ventilation correctly.
The sewer drain is best done in the floor.
Also put some fire extinguishers in the most accessible places, fires in laboratories alas happen.


The standard laboratory is usually equipped with technical devices and fixtures:
 For in-house production, it is advisable to use reactors with a volume of 50-200 liters. This volume allows you to organize the production of substantial batches. If necessary, several reactors can be used to increase the production.
For in-house production, it is advisable to use reactors with a volume of 50-200 liters. This volume allows you to organize the production of substantial batches. If necessary, several reactors can be used to increase the production.
- It is thermally resistant. Due to its low thermal expansion coefficient, it can withstand heat up to 500 °C and big temperature and pressure fluctuations;
- Smooth, with low adhesion, so that products made of it are easy to clean;
- does not absorb reagents, moisture and odors;
- durable, it is relatively difficult to break;
- has a high transparency, as a result of which it is convenient to observe the course of processes in the vessel.
All these properties are also important for other elements used in apparatuses. This glass is used to produce refrigerators, flasks, funnels, lids, pipettes and other components of reaction apparatuses.
The basic equipment of a laboratory borosilicate glass reactor usually includes:
- Reactor vessel with thermostatic jacket and bottom valve;
- Exchangeable lid, which is chosen depending on the number of elements to be connected;
- Propeller or anchor agitator with a motor of common or explosion-proof design;
- A condenser for distilling the solvent;
- A container to collect the condensate;
- drip funnel;
- Mobile frame on wheels with brake mechanism.
Glass vessels and other devices for laboratory installations are often made with ground connections. Grinded elements ensure tightness, so they are widely used in laboratory reactors. There are also screw and flange connections, connection with rubber tubes or special plugs.
In addition to borosilicate glass reactors, steel and fluoroplastic reactors are also used.
 Vacuum nutsche filter is a specialized device for vacuum filtration of liquid media, plant extraction. It is based on a single-layer reactor. It is a construction consisting of:
Vacuum nutsche filter is a specialized device for vacuum filtration of liquid media, plant extraction. It is based on a single-layer reactor. It is a construction consisting of:
- large stainless-steel funnel;
- A narrow glass spherical container for collecting filtrate;
- A steel mounting frame with fasteners;
- a support for the flask.
The upper part of the funnel is made in the form of a cylinder, with a stainless-steel grid built into its bottom - filtering material is placed on it. The tank neck is connected to the funnel by fasteners with screws. The seal between the flask and funnel is resistant to chemicals.
The glass flask has a valve for evacuating air (on top) and a valve for draining the filtrate (mounted on the bottom outlet). Made of high-quality glass. Faucet can be glass or teflon.
The frame is mounted on wheels for easy movement around the room.
This article describes a nutsche filter with a glass flask and metal funnel, but fluoroplastic, metal and ceramic nutsche filters are also used.
In the laboratory, usually use nutsche filters with a volume of 20 liters or more.



 The chemically resistant vacuum pump is designed for vacuum generation of different levels, for vacuum filtration and vacuum aspiration, gel electrophoresis; for connection to Nutche filters, evaporators, chemical reactors, glove boxes, medical suction boxes, drying and vacuum cabinets and other vacuum devices.
The chemically resistant vacuum pump is designed for vacuum generation of different levels, for vacuum filtration and vacuum aspiration, gel electrophoresis; for connection to Nutche filters, evaporators, chemical reactors, glove boxes, medical suction boxes, drying and vacuum cabinets and other vacuum devices.
A vacuum pump made of special chemically resistant materials with corresponding labelling are required for laboratory use. Depending on the design, vacuum pumps are of the following types:
-rotary vane oil pump;
-diaphragm piston pump;
-water circulating pump
and others...
 For laboratory reactors, heating circulation thermostats are used to maintain the set temperature in the jacket of the chemical reactor thanks to an integrated pump. The smaller the volume of the bath, the faster the heating of the coolant inside it, i.e. the external reactor will receive a fresh batch of coolant of the set temperature faster. The higher the heating capacity, the quicker the temperature control will be.
For laboratory reactors, heating circulation thermostats are used to maintain the set temperature in the jacket of the chemical reactor thanks to an integrated pump. The smaller the volume of the bath, the faster the heating of the coolant inside it, i.e. the external reactor will receive a fresh batch of coolant of the set temperature faster. The higher the heating capacity, the quicker the temperature control will be.
The heating thermostats have a steel, thermally insulated bath that allows the fluid to be safely heated up to 300 °C.
A peating сirculation thermostat is needed when the reaction mixture must be heated during the synthesis process.
 To cool the heat exchangers in chemical reactors, a chiller is a circulating cooler used to extract heat from the process. In contrast to the use of running water, the desired temperature can be for -20 °C.
To cool the heat exchangers in chemical reactors, a chiller is a circulating cooler used to extract heat from the process. In contrast to the use of running water, the desired temperature can be for -20 °C.
The chillers have both water (symbol "w") and air cooling of the refrigeration system. Chiller models (cooling thermostats) with water-cooled refrigeration system are quiet and require a small amount of cooling water, even at full cooling capacity. The chillers can be additionally equipped with a heater and an independent over-temperature protection. The maximum working temperature is increased to 100 °C and the temperature stability is ±0,2 °C.
A chiller is necessary if the reaction mass has to be cooled during synthesis.
 A deep freezer will be needed for cooling reagents that need it; for making ice; for sedimentation of obtained substances from the reaction mass after acidification and other similar processes.
A deep freezer will be needed for cooling reagents that need it; for making ice; for sedimentation of obtained substances from the reaction mass after acidification and other similar processes.
Freezers are divided into domestic and laboratory freezers and are very different in price.
The main requirements for laboratory freezers are:
- High accuracy of temperature setting.
- Homogeneity of temperature distribution throughout the entire volume of the freezer.
- Ability to install devices which register temperature changes in the cooling chamber and record the results on paper or electronic media (gauges, electronic or paper recorder).
- Availability of ports for validation of the refrigerator.
- Corrosion resistance of internal and external surfaces of the laboratory refrigerator to the action of aggressive detergents and disinfectants.
But for most home laboratories, normal freezers with a temperature range down to -20 ºC will do, so whether it makes sense to overpay for a laboratory freezer is up to you to decide.
 The rotary evaporator is a device for rapid removal of liquids by distillation at reduced pressure. Widely used in chemical laboratories for evaporation of solvents from mixtures of substances, as well as for the separation of liquids.
The rotary evaporator is a device for rapid removal of liquids by distillation at reduced pressure. Widely used in chemical laboratories for evaporation of solvents from mixtures of substances, as well as for the separation of liquids.
Not every laboratory can use a rotary evaporator. Before ordering a rotary evaporator, study the synthesis process in detail and determine if you need one.
 In the process of work in the laboratory there is a lot of dirty laboratory glass and other containers, to maintain cleanliness it is necessary to wash dirty objects. To accomplish this, order a deep metal sink like the ones they put in cafeterias to wash dishes. They are deep enough to wash large containers in them. In addition to the faucet, it is recommended to install a long hose for easy washing.
In the process of work in the laboratory there is a lot of dirty laboratory glass and other containers, to maintain cleanliness it is necessary to wash dirty objects. To accomplish this, order a deep metal sink like the ones they put in cafeterias to wash dishes. They are deep enough to wash large containers in them. In addition to the faucet, it is recommended to install a long hose for easy washing.

It is best to use a laboratory table made of metal, the size of the table is determined based on the area of the room and the location of the equipment. It is easy to care for and is more stable and durable, this allows you to use it with a heavy load.
 For storage of laboratory utensils and all kinds of items it is recommended to use a metal shelving unit, it is easy to use and durable, can withstand heavy loads. The rack will help to eliminate the clutter that can lead to dangerous consequences in the laboratory.
For storage of laboratory utensils and all kinds of items it is recommended to use a metal shelving unit, it is easy to use and durable, can withstand heavy loads. The rack will help to eliminate the clutter that can lead to dangerous consequences in the laboratory.
 If your home will be under video surveillance, we recommend placing several surveillance monitors in your home so that you can monitor your area from everywhere. One of them should be installed in the lab so that you can monitor your movements around your territory and during synthesis.
If your home will be under video surveillance, we recommend placing several surveillance monitors in your home so that you can monitor your area from everywhere. One of them should be installed in the lab so that you can monitor your movements around your territory and during synthesis.
To control your territory and access to it, we recommend installing a set of video cameras: to take under video control the road leading to the house; perimeter cameras; cameras at the entrances to the premises.
If you install IP cameras, you can monitor remotely.
It is also recommended installing an alarm system with a GSM module, so that when you open doors and windows in your premises, you get a signal on your cell phone and are aware if someone has entered them.
The electrical control panel that powers the entire lab should be right outside the door. In case of unforeseen circumstances that are impossible or dangerous to influence, you must run out of the lab and de-energize it from the safety of the door.
If you have windows in the laboratory, it is better to cover them with a thick multi-layered cloth or cover them with plastic panels.
The laboratory must be as equipped as possible: hot and cold running water, sewerage, heating/air conditioning, good electrical power (calculated total capacity of all devices with reserve). A backup generator, preferably with autostart in case of mains voltage drop, or an uninterruptible power supply inverter (preferably both devices) should ensure uninterrupted power supply to the laboratory. In some phases of synthesis, a short power outage can mean loss of productivity and create an explosion or fire hazard situation.
In the laboratory you need to put a good system of supply and exhaust ventilation, and I recommend putting a motor for exhaust ventilation twice as powerful as it is necessary for your room.
Draw in advance a diagram of the arrangement of devices in your laboratory to conduct power, water and ventilation correctly.
The sewer drain is best done in the floor.
Also put some fire extinguishers in the most accessible places, fires in laboratories alas happen.
The standard laboratory is usually equipped with technical devices and fixtures:
The main part of a laboratory reactor is a reaction flask made of chemically and thermally stable material. One such material is borosilicate glass. It has high physical and mechanical properties:- It is thermally resistant. Due to its low thermal expansion coefficient, it can withstand heat up to 500 °C and big temperature and pressure fluctuations;
- Smooth, with low adhesion, so that products made of it are easy to clean;
- does not absorb reagents, moisture and odors;
- durable, it is relatively difficult to break;
- has a high transparency, as a result of which it is convenient to observe the course of processes in the vessel.
All these properties are also important for other elements used in apparatuses. This glass is used to produce refrigerators, flasks, funnels, lids, pipettes and other components of reaction apparatuses.
The basic equipment of a laboratory borosilicate glass reactor usually includes:
- Reactor vessel with thermostatic jacket and bottom valve;
- Exchangeable lid, which is chosen depending on the number of elements to be connected;
- Propeller or anchor agitator with a motor of common or explosion-proof design;
- A condenser for distilling the solvent;
- A container to collect the condensate;
- drip funnel;
- Mobile frame on wheels with brake mechanism.
Glass vessels and other devices for laboratory installations are often made with ground connections. Grinded elements ensure tightness, so they are widely used in laboratory reactors. There are also screw and flange connections, connection with rubber tubes or special plugs.
In addition to borosilicate glass reactors, steel and fluoroplastic reactors are also used.
- large stainless-steel funnel;
- A narrow glass spherical container for collecting filtrate;
- A steel mounting frame with fasteners;
- a support for the flask.
The upper part of the funnel is made in the form of a cylinder, with a stainless-steel grid built into its bottom - filtering material is placed on it. The tank neck is connected to the funnel by fasteners with screws. The seal between the flask and funnel is resistant to chemicals.
The glass flask has a valve for evacuating air (on top) and a valve for draining the filtrate (mounted on the bottom outlet). Made of high-quality glass. Faucet can be glass or teflon.
The frame is mounted on wheels for easy movement around the room.
This article describes a nutsche filter with a glass flask and metal funnel, but fluoroplastic, metal and ceramic nutsche filters are also used.
In the laboratory, usually use nutsche filters with a volume of 20 liters or more.
A vacuum pump made of special chemically resistant materials with corresponding labelling are required for laboratory use. Depending on the design, vacuum pumps are of the following types:
-rotary vane oil pump;
-diaphragm piston pump;
-water circulating pump
and others...
The heating thermostats have a steel, thermally insulated bath that allows the fluid to be safely heated up to 300 °C.
A peating сirculation thermostat is needed when the reaction mixture must be heated during the synthesis process.
The chillers have both water (symbol "w") and air cooling of the refrigeration system. Chiller models (cooling thermostats) with water-cooled refrigeration system are quiet and require a small amount of cooling water, even at full cooling capacity. The chillers can be additionally equipped with a heater and an independent over-temperature protection. The maximum working temperature is increased to 100 °C and the temperature stability is ±0,2 °C.
A chiller is necessary if the reaction mass has to be cooled during synthesis.
Freezers are divided into domestic and laboratory freezers and are very different in price.
The main requirements for laboratory freezers are:
- High accuracy of temperature setting.
- Homogeneity of temperature distribution throughout the entire volume of the freezer.
- Ability to install devices which register temperature changes in the cooling chamber and record the results on paper or electronic media (gauges, electronic or paper recorder).
- Availability of ports for validation of the refrigerator.
- Corrosion resistance of internal and external surfaces of the laboratory refrigerator to the action of aggressive detergents and disinfectants.
But for most home laboratories, normal freezers with a temperature range down to -20 ºC will do, so whether it makes sense to overpay for a laboratory freezer is up to you to decide.
Not every laboratory can use a rotary evaporator. Before ordering a rotary evaporator, study the synthesis process in detail and determine if you need one.
It is best to use a laboratory table made of metal, the size of the table is determined based on the area of the room and the location of the equipment. It is easy to care for and is more stable and durable, this allows you to use it with a heavy load.
To control your territory and access to it, we recommend installing a set of video cameras: to take under video control the road leading to the house; perimeter cameras; cameras at the entrances to the premises.
If you install IP cameras, you can monitor remotely.
It is also recommended installing an alarm system with a GSM module, so that when you open doors and windows in your premises, you get a signal on your cell phone and are aware if someone has entered them.
If you have windows in the laboratory, it is better to cover them with a thick multi-layered cloth or cover them with plastic panels.
The drying room is prepared for working with finished products. Usually, a room of 3 by 3 meters is enough, but depending on the volume of production, the area of this room may be different. In this room install a system of racks, for drying and crystallization of finished products.
For the drying room, it is important to create a microclimate: a constant temperature and dry air. Therefore, in addition to the standard equipment to maintain a constant temperature, a dehumidifier must be installed. It has a container to collect water from the atmosphere, which must be emptied when filled.

Racks for the drying room are better to use wide with deep shelves. To dry the finished product, it is recommended to install an infrared film heater on the shelves and cover them with thick plastic film. Moderate infrared radiation is excellent for drying the finished product.
 In the past, the drying room was equipped with a good exhaust ventilation and dried by airflow. But this type of drying has several disadvantages: if you have a large mass of finished product, it dries very long and the hood has to work non-stop for a long time, which creates a lot of noise and a large waste of electricity.
In the past, the drying room was equipped with a good exhaust ventilation and dried by airflow. But this type of drying has several disadvantages: if you have a large mass of finished product, it dries very long and the hood has to work non-stop for a long time, which creates a lot of noise and a large waste of electricity.
On this basis, we recommend equipping as described above.
For the drying room, it is important to create a microclimate: a constant temperature and dry air. Therefore, in addition to the standard equipment to maintain a constant temperature, a dehumidifier must be installed. It has a container to collect water from the atmosphere, which must be emptied when filled.
On this basis, we recommend equipping as described above.
The warehouse for precursors and chemical reagents does not have to be located in the house, it can be any outbuilding, such as a garage or a shed.
Different chemical reagents have different storage conditions, so be aware of this before setting up a warehouse. In hot climates, some reagents may require storage in a refrigerator or freezer.
The warehouse must be ventilated: for example, solvents tend to evaporate from canisters, and if enough vapors accumulate, a spark or high temperature is enough to spontaneously combust. It is also desirable to equip the warehouse with fire extinguishers or a fire suppression system.
For storage, you will need a system of shelving, as in the previous rooms we recommend using metal structures, as they are particularly durable and do not require special care.
You need to have filling/dispensing equipment, scale and empty containers in the warehouse to be able to measure the necessary number of reagents for syntheses, for subsequent transfer to the laboratory.


Different chemical reagents have different storage conditions, so be aware of this before setting up a warehouse. In hot climates, some reagents may require storage in a refrigerator or freezer.
The warehouse must be ventilated: for example, solvents tend to evaporate from canisters, and if enough vapors accumulate, a spark or high temperature is enough to spontaneously combust. It is also desirable to equip the warehouse with fire extinguishers or a fire suppression system.
For storage, you will need a system of shelving, as in the previous rooms we recommend using metal structures, as they are particularly durable and do not require special care.
You need to have filling/dispensing equipment, scale and empty containers in the warehouse to be able to measure the necessary number of reagents for syntheses, for subsequent transfer to the laboratory.
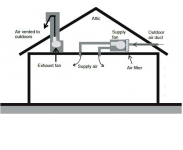
An excellent supply and exhaust ventilation system should be installed in the laboratory.
The supply and exhaust ventilation system is a complex of equipment that provides air intake from the street, it's cleaning from dust, pollen and supply into the room. At the same time, the second part of the system collects exhaust air and unpleasant odors and removes them outside.
Scrubbers are used for cleaning gaseous media from impurities in various chemical and technological processes, they are gas purification devices based on gas flushing with liquid.
Scrubbers are designed for capturing gases discharged from the reactor. The cleaning of gases from impurities by means of scrubbers belongs to the wet scrubbing method. This method is based on washing of gas with liquid (water, alkaline solution, and others) at the most developed surface of the liquid contact with aerosol particles and the most intensive mixing of the cleaned gas with liquid. This method allows removal of dust, smoke, mist and aerosol particles (usually unwanted or harmful) of almost any size from the gas.
The following types of scrubbers are distinguished:
- nozzle-type towers (nozzle-type scrubbers);
- sprayed cyclones (centrifugal scrubbers);
- foam apparatus;
- Venturi scrubbers.
The operation of wet gas scrubbers is based on capture of dust particles by the liquid, which carries them away from the apparatuses in the form of sludge. The collection process in wet dust collectors is improved due to the condensation effect - enlargement of dust particles due to condensation of water vapor on them.

The supply and exhaust ventilation system is a complex of equipment that provides air intake from the street, it's cleaning from dust, pollen and supply into the room. At the same time, the second part of the system collects exhaust air and unpleasant odors and removes them outside.
In order for the ventilation to work effectively, you must correctly calculate the capacity of the fans for the volume of your room. Wherein it is necessary that the power of the exhaust fan should be twice as much as the supply fan. In this case, the odors will be removed quickly.

Scrubbers are used for cleaning gaseous media from impurities in various chemical and technological processes, they are gas purification devices based on gas flushing with liquid.
Scrubbers are designed for capturing gases discharged from the reactor. The cleaning of gases from impurities by means of scrubbers belongs to the wet scrubbing method. This method is based on washing of gas with liquid (water, alkaline solution, and others) at the most developed surface of the liquid contact with aerosol particles and the most intensive mixing of the cleaned gas with liquid. This method allows removal of dust, smoke, mist and aerosol particles (usually unwanted or harmful) of almost any size from the gas.
The following types of scrubbers are distinguished:
- nozzle-type towers (nozzle-type scrubbers);
- sprayed cyclones (centrifugal scrubbers);
- foam apparatus;
- Venturi scrubbers.
The operation of wet gas scrubbers is based on capture of dust particles by the liquid, which carries them away from the apparatuses in the form of sludge. The collection process in wet dust collectors is improved due to the condensation effect - enlargement of dust particles due to condensation of water vapor on them.
Every laboratory faces the problem of waste disposal. There are three types of waste:
1. Gaseous.
2. Solids.
3. Liquid.
The gaseous wastes, as described above, can be discharged into the atmosphere with an exhaust ventilation or washed out with a flow of washing liquid in a scrubber.
Solid wastes are mostly containers and packages from reagents and equipment: plastic, paper (wood), metal, glass, and others.
If in the process of work you manage to reuse of these items, then certainly take advantage of it, rather than buy new ones. For example, glass jars can be washed and used for weighing or storage, as can some metal and plastic containers.
But some solid waste will still have to be disposed of, usually taken out and thrown away. To avoid being caught by the police, you should get rid of stickers and labels that identify the lot and the name of the product, which could eventually become evidence against you. To minimize the risks, you should erase or paint over the lettering, remove the stickers, and cut off the tags.
You can compact the solid waste; it will be more compact and easier to remove. Choose a place in advance where you will take the waste to be discarded. The disposal site should be a decent distance from the lab, if your waste is found and will arouse suspicion, then nearby homes and businesses will be checked.
Liquid waste is frequently discharged, leaving it in containers is risky, if detected, examination will show its relation to the synthesis of banned substances. Such waste is divided into two types: contaminated water and water insoluble waste organic solvents.
It is recommended that only contaminated water be discharged into the sewer system, as water insoluble substances can corrode pipes or clog the discharge, causing additional risks to the laboratory. Therefore, they should be taken far away from the laboratory and discharged. They can also be burned in a Diesel Heater.


In industrial plants, some waste is destroyed in incinerators, special gas furnaces. Incinerators come in small sizes and can be used in the laboratory, but will require a separate room or outdoor space.

Incineration is the process of combusting the organic elements within waste streams. Industrially, this process is also known as ‘thermal treatment’.
There are 2 main by-products of incineration. The first is inert bottom ash which is mostly formed by the in-organic elements of your waste stream, and the second is flue gas which providing the appropriate gas cleaning systems have been specified Is safe to let dispel into the atmosphere.
Parts of an Incinerator.
The parts of most incinerators are quite standard, the main factor when selecting these parts is their ability to last and operate well under the high-stress environments witnessed in incineration.
-Primary Chamber (Combustion Chamber) – this is where the waste is loaded and ignited. In most incinerators, the ignition occurs due to the high ambient temperatures being retained within the chambers lining.
-Secondary Chamber – sometimes also called the ‘afterburner’ chamber is required by law in Europe, USA, Australia and Canada prevents the formation of harmful particulates. In many countries, the law stipulates that all flue gas must be resident in this secondary chamber for at last 2 seconds at 850 ºC.
-Flue Stack – also known as the chimney. Most incinerators require a stack height of at least 3 m. This will be considerably higher in more built-up areas or where atmospheric conditions dictate.
-Control Panel & Thermocouples – these control the operation of the machine and ensure the chambers are up to temperature BEFORE any waste is loaded for incineration.
-Burners – Most modern incinerators are fitted with low NOx or modulated gas flow burners to increase.
-Fuel Tanks – Fuel tanks should be bunded to ensure safe storage of fuel.
 Incinerators are designed for the safe and effective decontamination of many types of waste. By using an incinerator with a high-quality afterburning chamber and dust and gas cleaning system, dioxin and furan emissions can be avoided in the waste gases.
Incinerators are designed for the safe and effective decontamination of many types of waste. By using an incinerator with a high-quality afterburning chamber and dust and gas cleaning system, dioxin and furan emissions can be avoided in the waste gases.
Incinerator is a furnace in which the incineration (thermal decontamination) of waste is provided at high temperatures of 400 to 1200 ºC.
1. Gaseous.
2. Solids.
3. Liquid.
The gaseous wastes, as described above, can be discharged into the atmosphere with an exhaust ventilation or washed out with a flow of washing liquid in a scrubber.
Solid wastes are mostly containers and packages from reagents and equipment: plastic, paper (wood), metal, glass, and others.
If in the process of work you manage to reuse of these items, then certainly take advantage of it, rather than buy new ones. For example, glass jars can be washed and used for weighing or storage, as can some metal and plastic containers.
But some solid waste will still have to be disposed of, usually taken out and thrown away. To avoid being caught by the police, you should get rid of stickers and labels that identify the lot and the name of the product, which could eventually become evidence against you. To minimize the risks, you should erase or paint over the lettering, remove the stickers, and cut off the tags.
You can compact the solid waste; it will be more compact and easier to remove. Choose a place in advance where you will take the waste to be discarded. The disposal site should be a decent distance from the lab, if your waste is found and will arouse suspicion, then nearby homes and businesses will be checked.
Liquid waste is frequently discharged, leaving it in containers is risky, if detected, examination will show its relation to the synthesis of banned substances. Such waste is divided into two types: contaminated water and water insoluble waste organic solvents.
It is recommended that only contaminated water be discharged into the sewer system, as water insoluble substances can corrode pipes or clog the discharge, causing additional risks to the laboratory. Therefore, they should be taken far away from the laboratory and discharged. They can also be burned in a Diesel Heater.
Incineration is the process of combusting the organic elements within waste streams. Industrially, this process is also known as ‘thermal treatment’.
There are 2 main by-products of incineration. The first is inert bottom ash which is mostly formed by the in-organic elements of your waste stream, and the second is flue gas which providing the appropriate gas cleaning systems have been specified Is safe to let dispel into the atmosphere.
Parts of an Incinerator.
The parts of most incinerators are quite standard, the main factor when selecting these parts is their ability to last and operate well under the high-stress environments witnessed in incineration.
-Primary Chamber (Combustion Chamber) – this is where the waste is loaded and ignited. In most incinerators, the ignition occurs due to the high ambient temperatures being retained within the chambers lining.
-Secondary Chamber – sometimes also called the ‘afterburner’ chamber is required by law in Europe, USA, Australia and Canada prevents the formation of harmful particulates. In many countries, the law stipulates that all flue gas must be resident in this secondary chamber for at last 2 seconds at 850 ºC.
-Flue Stack – also known as the chimney. Most incinerators require a stack height of at least 3 m. This will be considerably higher in more built-up areas or where atmospheric conditions dictate.
-Control Panel & Thermocouples – these control the operation of the machine and ensure the chambers are up to temperature BEFORE any waste is loaded for incineration.
-Burners – Most modern incinerators are fitted with low NOx or modulated gas flow burners to increase.
-Fuel Tanks – Fuel tanks should be bunded to ensure safe storage of fuel.
Incinerator is a furnace in which the incineration (thermal decontamination) of waste is provided at high temperatures of 400 to 1200 ºC.
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: